- EXPLORE FURTHER: Important indicators of colon cancer following the 'disturbing increase' among younger individuals
Consuming vitamin D might assist in preventing colon issues. cancer , Hungarian research suggests.
The nutrient was associated with decreasing the likelihood of contracting the disease as well as enhancing the outcomes for those who still developed it, according to the researchers.
Commonly referred to as the 'sunshine vitamin,' individuals obtain Vitamin D through sun exposure and also via food sources such as fatty fish, red meat, and egg yolks.
The researchers behind the latest study cautioned that Europeans, particularly city dwellers, faced a higher likelihood of experiencing deficiencies.
As such they highlighted the potential use of vitamin D supplements, available for about 2p per pill at high-street pharmacies.
Their discoveries come as colon cancer cases have mysteriously increased among younger people, with diagnoses rising by 80 percent over three decades.
A recent study by Hungarian researchers examined 50 prior investigations encompassing over 1.3 million patients.
They discovered that individuals with sufficient levels of vitamin D had a reduced chance of developing colon cancer by 25 to 58 percent.
The study also revealed that consuming an additional 2.5 micrograms of vitamin D through supplements was associated with a 4 percent decrease in the risk of developing colon cancer.
The NHS suggests that both adults and children aged one year and older should consume 10 micrograms of vitamin D daily.
The Hungarian review similarly discovered indications that individuals suffering from colon cancer who possessed elevated amounts of the vitamin experienced more favorable results.
Specialists referenced a study which discovered that late-stage colon cancer patients who received a high daily dosage of vitamin D survived an additional two months on average.
Previous research has indicated that individuals diagnosed with bowel cancer, also known as colon cancer, who exhibit elevated levels of vitamin D face a 50 percent lower risk of succumbing to the illness.
The researchers suggest that Vitamin D could offer anticancer advantages by reducing inflammation, which might initiate alterations leading to cancer. Additionally, it appears to assist in eliminating cancer cells and impeding tumor development through enhancing the body’s immune response.
The study's author, Professor János Tamás Varga from Semmelweis University, informed Fox News Digital 'Vitamin D is essential for both preventing and treating colorectal cancer.'
He stated: "These findings indicate that the impact of vitamin D could be influenced by variables like dosage, the specific health status of the patients, and the length of the therapy."
In the research paper, which appeared in the journal Nutrients The experts similarly emphasized the significant vulnerability many individuals face regarding Vitamin D deficiency.
'They noted that urban populations face higher risks due to limited sunlight exposure caused by air pollution and crowded buildings.'
This was particularly noted as a concern for European communities.
"About 40 percent of Europeans are deemed to have insufficient levels of vitamin D, with 13 percent categorized as having severe deficiency," they noted.
As much as 40% of British adults might experience vitamin D deficiency during winter due to reduced sunlight exposure.
Hungarian specialists remained assured about the connection between vitamin D and the prevention and treatment of colon cancer but admitted that their research was not without certain constraints.
They observed that the studies included in their analysis employed varying doses of vitamin D and encompassed patients at different phases of cancer development.
Therefore, they concluded that additional studies were necessary to establish the ideal potential dose of vitamin D and assess its efficacy.
Scientific discussions continue regarding the connections between vitamin D and the prevention of cancer.
The charity Cancer Research UK (CRUK) indicates that although studies continue, they have found insufficient proof suggesting that lacking vitamin D significantly raises the likelihood of developing cancer.
The organization further states that there is still no concrete evidence suggesting that consuming a vitamin D supplement can help prevent cancer specifically.
Data from the charity indicates that bowel cancer, often referred to as colon cancer, has experienced a 52 percent rise in occurrence among individuals between the ages of 25 and 49 since the early 1990s.
Certain researchers propose that heightened pollution could be responsible, whereas others argue that the pattern can be attributed to escalating consumption of highly processed foods.
While CRUK acknowledges the increase, they emphasize that bowel cancer cases among younger individuals remain relatively rare, with approximately one out of every 20 diagnoses occurring in those below the age of 50.
Approximately 2,600 new instances of colorectal cancer occur annually in individuals between the ages of 25 and 49 in Britain, with roughly 44,100 new cases reported across all age groups.
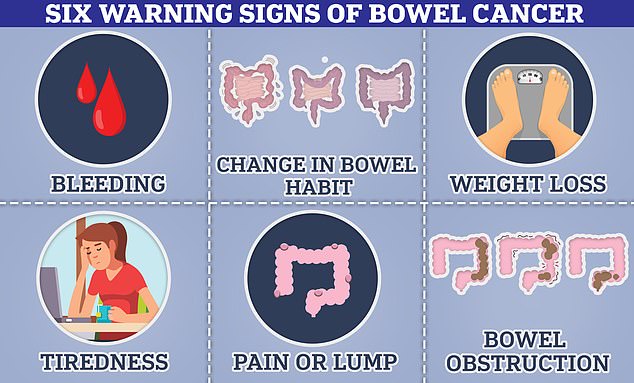
The symptoms of colorectal cancer encompass alterations in bowel habits like diarrhea or constipation, an increased or decreased urgency to defecate, presence of blood in the feces, abdominal discomfort, bloating, unexplained weight loss, and feelings of tiredness.
Vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphate, which are essential nutrients for maintaining healthy bones, teeth, nerves, and muscles.
It also aids in maintaining proper function of the immune system.
The absence of this vitamin can result in bone issues such as rickets, which is characterized by bone pain, weakened bones, and potential deformities.
According to the NHS, most individuals can obtain the necessary amount of vitamin D from sunlight during the period from April through September.
Nevertheless, during the gloomier months, it is recommended for all British adults and children above the age of one to take a vitamin D supplement to maintain adequate levels.
Certain individuals are encouraged to think about consuming supplements on an ongoing basis.
This encompasses individuals with deeper skin pigmentation — which leads to lower levels of vitamin D absorption — along with those who are homebound and receive limited exposure to natural sunlight.
However, one must be cautious not to consume excessive amounts of vitamin D.
The NHS cautions that consuming excessive amounts of vitamin D over an extended period can have adverse effects on our well-being.
Since vitamin D aids in absorbing calcium, excessive amounts can lead to a condition known as hypercalcaemia.
Ironically, this can lead to weakened bones and also harm the kidneys and heart.
Consequently, the NHS advises individuals not to consume more than 100 micrograms of vitamin D daily without specific guidance from their physician.
The level of vitamin D in your system can be assessed through a blood test — with the findings expressed in nanomoles per liter, denoted as nmol/L.
A vitamin D level of 25 nmol/L or less is regarded as deficient—this threshold was established around two decades ago when it was associated with a higher chance of developing rickets.
Read more

%20(1024%20x%201024%20piksel)%20(1).png)
%20(1024%20x%201024%20piksel)%20(5).png)

%20(1024%20x%201024%20piksel)%20(1).png)
0 Comments